Summary of Generalized Space-Time Relativity
----Explore about Einstein’s Relativity
(Author:Xia Xingguang)
Abstract
This article briefly describes the logic and conceptive errors in Einstein’s relativity and the basic viewpoints of the Generalized Space-Time Relativity. And points out that Generalized Space-Time Relativity is a new space-time theory, which is established on the basis of the dialectical materialist point of view on space and time. Starting from this theory, not only some theoretical results of Einstein’s two relativities can be generated under given conditions, but also some academic achievements have been obtained in the known branches of learning.
I The Problems as Proposed
As early as 1908 when physics was rapidly developing, Lenin
pointed out sharply that “ordinary scientists and those in the field of physics
were on the majority standing for the dialectical materialism, but a few mew
physicists, who were affected by the collapsed oil theories due to recent important
discoveries, especially the crisis of the new physics caused by the relativity of our
knowledge, ran into relativism and eventually into idealism… (Refer to [1],
Pages 359-360) ”.
Despite of this and the great victories won by dialectical materialism in every aspect, in the present natural science, subjective idealism is still widely spreading. The commentary to the scientific and educational movie “The Universe And The Man” says, “… The time and space of the universe are changing because mass, energy and speed in the universe are changing. … When atomic nucleus is approaching the velocity of light, electron will gradually reach its speed limit and revolve the more the slowly. This means the vibration of electron goes down. Life is controlled by electron, so the living pace can be slowed down, naturally the same with time. That is to say, human beings can prolong their life by simply quickening the velocity. If we could live ten thousand years as one day, it would be nothing to travel around the universe. So, the secret of longevity of the human beings just lies in the velocity.” Obviously, this view comes out of Einstein’s special theory of relativity. According to the relativity in narrow sense, the time coordinates(t’)and the space coordinates(r’)will in the process of movement result in “Lorentz’s constriction”. According to this so-called “constriction”, the paradox---- “twin paradox”---- can be deduced. If the existence of Lorentz’s constriction were acknowledged,it would mean that Time and space are not objective existence, but the directly perceived form of people’s sensitivity.(refer to [2], page 45. Markedly, this is Kant and Mach’s relativist point of view on time and space and pure subjective idealism.
If we take these views as scientific imaginations to raise people’s interest in scientific research, it is worth thinking. But if these views are disseminated through a scientific and educational movie, it is worth argumentation. Of course, I don’t mean to say that the director to this movie is deliberately publicizing idealism, but to say that in the current space and time theory, there is a wide existence of the ideological tendency of subjective idealism.
In addition, in this movie, the theory of the universe created out the “big-bang” is aired as a mature theory. It can said definitely that, in the cosmography, big-bang cosmology is not a mature and dependable point of view, for there lies a logic error in this view that is difficult to overcome.
As it is known to all, the experiment data of this view come from “phenomena of red shift of spectrum” that was discovered by Hubble an American astronomer (1930). Currently, the authoritative interpretation of this phenomenon is the universe model of the big-bang. This interpretation is based on “Doppler effect” and the theoretical basis of Doppler effect is Einstein’s general theory of relativity (refer [3], pages 479~489). According to this model, our universe is created out of an unprecedented “big-bang”. The resulting “fragments” after explosion ----the stellar system----fly out to all directions in a velocity close to the velocity of light. It can be generated that the universe to date is aged about 15 billion years old.
With reference to this explanation, we can make an obvious logic reasoning: Observing from the earth, we can see the stellar system is “red shift” on the azimuth of 3600 in the great circle of the celestial sphere. If it were so, the earth would be naturally the core of the “explosion”. However, this is absolutely impossible. Not to mention the earth, even the solar system and the Milky Way galaxy is only a tiny part of the vast universe. How come the earth becomes the core of the explosion within the vast universe? One can imagine, if the celestial body on which we are living were not the solar system in the Milky Way galaxy, but another stellar system outside of the Milky Way galaxy, and we still use the Hubble telescope to observe the existing interplanetary space, it must turn out that all the stellar systems are circling around a core celestial body and continuously dispersing outwards. For this ‘swelling process” of the universe, some people made a vivid comparison with the blowing of balloon, thinking that separation between the stellar systems is like two “physical points” located on the balloon, as the balloon swells, the distance between the two points will become larger and larger. At this, people would ask, where does the person observing the swelling universe stand? Can he/she stand outside of the universe to observe the universe? Is the earth not within the universe? So, there exist some unconquerable logic errors when using Doppler effect to explain the phenomena of red shift of spectrum.
In nature, using this view to explain the formation of the universe isn’t better than Ptolemy’s theory that the earth is the core of the universe. Obviously, this view brings the issue back onto the old road of “religionism”. Of course, it is not impossible for any partial galaxy to explode due of “collapse of gravitation”, even this explosion may create other new galaxies, such as solar system, Milky Way galaxy, etc. But, any given “stellar system” cannot represent the “universe”, for according to the dictionary explanation, limitless “time” is the universe; limitless “space” is the universe. So, the so-called “universe” is only a byname of space and time. As a result, the law of evolvement of any stellar system in the sense of limited space and time cannot represent the law of creation of the universe by itself.
II Logic and Conceptive Errors in Einstein’s Relativity
The reason why this situation occurs is that, from the very beginning, Einstein’s relativity adopted the physical conceptions and principles of Newton’s mechanics, including inertial frame, relative velocity, Galileo’s principle of relativity, invariability of velocity of light, etc. As it is known, “inertial frame” puts the observer and the clock recording the time process on the “coordinate origin” (O) of the reference frame, while the “relative speed” is to divide the time process(t)recorded by the “resting clock” located on the “coordinate origin” (O) of the reference frame by the space distance of the moving thing (r), i.e., V = r/t. Of course, in Newton’s mechanics, it no problem to define the reference frame and the relative speed, because it is assumed that the transmitting velocity acting on each is infinite, time has absolute simultaneity and the reciprocity of two objects is exceed space. It is because this assumption does not comply with the reality that there are some congenital deficiencies lying in Newton’s mechanics, thus making it a space-time theory that is approximately correct.
One principle that must be pointed out is the most elementary logic principle that has to be followed in precisely determining/recording some physical quantity including time, i.e. contact action principle. In other words, either to determine the space location (space coordinates) of a moving thing or to determine the correct time that the moving thing arrives at the space location (time coordinates) must be realized by some sort of contact----if it is not the observer’s direct contact with the moving thing, it must be the moving thing transmitting the movement information through some sort of signal. Without any form of contact, there would be no precise determination of the physical quantity. So in Newton’s mechanics, within one inertia frame, the use of one clock to precisely determine the time coordinate of a moving thing (or particle) at any space location after leaving the coordinate origin is certainly established on the exceed space action principle. On the basis of exceed space action principle; physical quantity can only be determined through abstract thought. It is not difficult to understand that the practice of determining physical quantity by means of abstract thought is, on the objective side, equal to fully admitting the assumption that signal transmitting velocity is infinite!
The reality of the universe is : The limit velocity of transmission acting on each other equals the velocity of light in vacuum whereas the velocity of light is a finite constant(c = 2.99793x1010cm/s)---- Invariability of the velocity of light. Therefore, the under premises of the limit velocity of transmission acting on each other and contact action principle, some variation will unavoidably appear to the inertial frame, relative velocity, Galileo’s relativity theory, etc. The reason is: under this situation, neither the observer located on the coordinate origin (O) of the relatively resting inertial frame (K) nor the observer located on located on the coordinate origin (O’) of the relatively moving inertial frame (K’) would use their clock to give out simultaneously the time coordinates (t2 and t2’) of the moving thing (or particle) while they are relatively moving in any speed (and any space distance). When we use light signal (or electromagnetic wave) to determine the time coordinates of the moving thing (or particle), these time coordinates (t2 and t2’) will always contain the “movement information” of the moving thing (or particle) that arrives at any time location, the delayed time process needed to use the velocity of light to transmit to the observer at the starting point of movement----we record these time processes asΔt2 andΔt2’. It must be pointed out, the non-synchronization mentioned here does not mean any variation that appears between the “moving clock” and the “resting clock” on the circle of vibration, but refers to the fact that the time coordinates (t) recorded by the resting observer for the moving thing always contains the delayed time process(Δt). In detail, the observers standing respectively at the coordinate origins (O and O’), while recording the moving thing (or particle), must on their own contain a delayed time process (Δt2 andΔt2’ ) needed to transmit the movement information by the velocity of light.
However, in Einstein’s relativity, neither the time coordinates(t’)on the movement system(K’) nor the time coordinates(t)on the stillness system(K)contain such a delayed time process; Particularly in the special theory of relativity not only is this the case, but also consideration is given to the comparison of the time and space coordinates for two moving things, which do not share a “common starting point”----to carry out coordinate transform. Obviously, this coordinate transform has violated the elementary logic principle that has to be followed while making mutual comparison. Actually, in making comparison, “Difference (or diversity) is such that different things are independent of each other in their original forms and do not affect each other while interacting with each other, so this interactive relationship is extrinsic to both parties. Because the difference of things does not affect them and is foreign to their nature, it becomes a third party outside the things involved, i.e., a comparer. Such outside difference that according to they are oneness of correlative thing to consider, they are equal; according to they are Difference of correlative things to consider that they are not equal. (Refer to [4], page 251)” Therefore, in the special theory of relativity, any difference between t & t’ and r& r’ is a result of the subjective discretion of the comparer.
In a word, one inevitable thinking logic is: if the two observers standing at the coordinate origins(O and O’)on the two relatively moving reference frames (K and K’) can use their own clocks to give out, in absolute synchronism, the time coordinates (t2 and t2’) for a given object (or particle) moving relatively in any velocity (including the velocity of light) and any space distance (including astronomical distance), these two observers must do this by their thinking ability (imaginary infinite signal velocity) without giving consideration to the delayed time process (Δt2 and t2’). Thereupon, t’≡t. As a consequence, the time conception of “absolute simultaneity” is not cast off and we are brought back to Newton’s mechanics. Obviously this runs in the opposite direction to the basic fact that is the limit velocity of transmission acting on each other. For instance, in the object system of the sun, earth and moon, from the theoretical point of view, if the observer standing on the earth and the observer standing on the sun can send out, in absolute synchronism, the time coordinates (t' and t) to the moon respectively in their relative space location on the movement, there must exist an absolute simultaneity among the moon, the earth and the sun. Obviously, the formal logic of this issue is: if A = C,B = C,then A = B. In Einstein’s relativity, the assumption used to calibrate the clocks of the two locations does not give consideration to the delayed time process (Δt2 andΔt2’). So, Einstein’s relativity never breaks away with the time conception of absolute simultaneity. ----This is both an important physical problem and an important philosophical problem!
III Essentials of Generalized Space-Time Relativity
Theoretically, any moving thing (or particle) is an “object system”, same as the inertial frame. We might as well call them the “third object system”. The principle herein is: as long as object systems exist, it can be regarded that there are observers and the clocks recording the movement process on these object systems. By this, the concept of relativity is not: the observers stand the coordinate origins(O and O’)of coordinate system(K and K’)which relatively move, who have an intercomparsion between two kinds different time-space coordinates, then third object system moves relatively to them(K and K’); and is not: relative moving of each “opposite” to “himself”, that between observer stands on the origin(O’)of relative moving coordinate system(K’)and observer stands on the origin(O)of relative resting coordinate system(K), who carried out intercomparsion between such two different “space-time coordinates”. Because, for mutual comparisons in these two aspects, the former does not break away with the time concept of absolute simultaneity while the later goes even far to replace the physical concepts beyond that applied to the former. Either of them regards themselves as in the resting system and the other as in the moving system. In reality, this is not the same moving thing.
There from, the concept of relativity can only be: the observer standing at the origin(O)on the relative resting reference frame (K) who observes the movement on the moving system (K’) corresponding to the coordinate origin (O) and obtains a “space-time coordinates”; the observer standing at the origin (O’) on the relatively moving reference frame (K’) who observes his own relative movement corresponding to the coordinate origin (O) on the resting reference frame(K) and obtains another “space-time coordinates”; The comparison of the two types of time coordinates and the two types of moving velocity----the transform of coordinates----then constitutes the concept of relativity. But the relativity in this sense is not Einstein’s relativity, and is the Generalized Space-Time Relativity, which is established on the basis of the dialectical materialist concept of space and time. Over here, the meaning of “Generalized Space-Time ” is: first, time and space represent in concept the universality of the “form of existence” and the “process of moving” of things; secondly, we carry on Riemann’s assumption that “the integration of similar phenomena constitutes a rifeness space”.
A right case in point is one person (A) standing still in Beijing Airport and another person (B) flying to New York of the United States. At the time of department, both men set their timepiece. The time recorded by Beijing timepiece is represented by t while the time recorded by the plane timepiece is represented by t’. Our precondition is both timepieces are absolutely of the same time recording performance. Sure, after departure, both men can only use their own timepiece to record the time process t and t’ as experienced by the flying plane. By the time when the plane lands in New York after some time, B can tell the exact time of arrival as recorded by the plane timepiece in absolute synchronism (say, the total flight time is: t’=10 hrs). However, A cannot tell in due course the exact time of arrival of the plane in New York unless he asks B to tell him the time when B arrives in New York through the quickest means of communication. In this universe, the fastest velocity to transmit the movement information of the objects is just the velocity of light in vacuum (c = 2.99793×1010cm/s). So, presently we use this limit velocity to calculate the time process needed to transmit the movement information of objects. Obviously, the time process needed by B to tell A the movement information of the plane arrival in New York is: Δt =r/c. So, there lies a concept change. According to our normal experience, A would think in the same way that the flight time from Beijing to New York needs 10 hours, i.e., the time process in both A and B’s view is absolutely the same. In other words, if the set departure time is 00:00, then t = t’ = 10 (hrs). This ideology is nothing problematic if it is not considered in relativity, but it needs change to the opposite, because what discussed by relativity is two observers (A and B) in different locations describing the movement process of the same object (e.g., plane in this case). What to be considered here is that the flight time (t) as recorded by A must include the minimum time process (Δt) used for information transmission. If the direct distance from Beijing to New York is represented by r, the time process recorded by the plane timepiece is represented by t’, and the plane is flying at an even velocity, then t = ( t’ +Δt). In this way, A gets the relative velocity of the plane V = r / (t’+Δt) while B gets the absolute velocity of the planeυ= r’/t’. Clearly, only the absolute velocity can precisely reflect the moving velocity of the plane, whereas the relative velocity contains the time process (Δt) needed for transmitting the movement information and therefore is not a precise physical concept.
IV Invariability of the Velocity of Light
When we come down to the issue of relativity, we cannot go without touching the invariability of the velocity of light. It can be said that the velocity of light invariability principle is one of the important conditions for judging whether Einstein’s relativity is correct or not. When we talk about the velocity of light invariability principle, we cannot go without touching the method used to measure the velocity of light. As it is known, in the traditional method to measure the velocity of light, the observer always stays at the location of light source (on the resting system) and takes half the time process (e.g., 2t/2=t) traveled by the photon between the light source and the reflector as the time process needed for transmission on the space distance (r), so as to get the relative velocity of photon transmission c = r/t. It is not difficult to see, this method of measurement fully equals the time process (t’) recorded by the observer’s own timepiece at any time when he is traveling with the photon and divided by the space distance (r’), i.e., c’= r’/t’ (temporarily recorded as c’). Here, c’ is defined as the absolute velocity of the moving photon, so the relative velocity (c) of the moving photon as measured by the traditional method is of the same physical quantity as the absolute velocity of the moving photon measured by the observer standing on the photon, i.e., c ≡c’. It is noticed that the space distance between “light source” and “reflector” is of the same physical quantity for the observer standing at the light source and at the reflector, i.e., r ≡r’. Therefore, there exist two types of velocity of light: one is the relative velocity of the moving photon as obtained by the observer standing at the light source, i.e., c = r/(t’+Δt) while the other is the absolute velocity of the photon relative to the moving light source as measured by the observer who is moving together with the photon, i.e., c’ = r’/t’. Because r ≡r’, so c ≠c’. In this way, it is not difficult to see, the absolute velocity (c’) of the moving photon has nothing to do with the relative velocity of the moving light source. This is just like the case where the absolute velocity of the bullet leaving the gunpoint has nothing to do with the relative velocity of the gun itself relative to other reference. Obviously, the so-called “velocity of light invariability principle” is that the absolute velocity(c’)of the photon relative to the moving light source does not change, but not that the relative velocity(c)of the photon relative to the moving light source does not change. So to conclude, the way to use one’s own thought to determine the time coordinates of the photon at any space location is fully equal to the assumed precondition that the velocity of transmission acting on each other is infinite. Therefore, the traditional method to measure the velocity of light is established on the concept of absolute simultaneity. ---This is a common physical issue that requires thorough consideration and repeated elaboration!
V Mathematic Model of the Generalized Space-Time Relativity
Based on above consideration, we say, the comparison between the two time processes(t and t’)recorded and the two flight velocities(V andυ)obtained by the two observers at two different locations for the plane flying from Beijing to New York----transform of coordinates---is the relativity of A (relative still observer) about the moving process of the plane (object). Because the space distance(r and r’)from Beijing to New York is of the same physical quantity for A (still observer) and B (moving observer), the relatively moving observer can write out his “interval square” as follows according to the “classical definition”:
Δs’2 = c2(t’2 – t’1) 2–Δr’2 = 0 (1)
While the relatively still observer can equally write his “interval square” according to the definition as follows:
Δs2 = c2(t2 – t1)2 –Δr2 ≠ 0 (2)
In (1),
Δr’ 2= (x’2 – x’1)2 + (y’2 – y’1)2 + (z’2 – z’1)2 (3)
While in (2),
Δr2 = (x2 – x1)2 +(y2 – y1)2 +(z2 – z1)2 (4)
Here, Δr’ is the observer standing on the moving frame (K’), using Descartes’ coordinates to show the “space distance’ of the moving thing from the “starting point” to the “end point”, whileΔr is the observer standing on the resting frame (K), using Descartes’ coordinate to the “space distance’ of the same moving thing from the same starting point to the end point. When the two objects (or observers) are infinitely close to each other in distance, the interval square (Δs’2 andΔs2) can be re-written in differential formula, i.e.,
ds’ 2 = c2dt’2– dx’2– dy’2– dz’2 = 0 (5)
And
ds2 = c2dt2– dx2– dy2– dz2 ≠ 0 (6)
On the surface, the interval square (Δs’2
andΔs2) as obtained by the relatively moving observer and the
relatively still observer are different to each other, but this difference is the
relativity of the observation results for the time coordinates caused only by different
locations. Contrary to Einstein’s special theory of relativity, the Generalized
Space-Time Relativity holds the view that the objective causes leading to the difference
of the time coordinates is the finiteness of action principle transmit velocity rather
than the “Lorentz’s constriction” that is assumed to exist in reality.
Self-evidently, if the transmit velocity of action principle is infinite, no matter how
far the two observers stand apart, it would not appear that t ≠ t’. Therefore, it is
pure subjective assumption that causes inequality of the interval square. It is on account
of this that we can use the synthetical proposition formulated on the basis of dialectical
logic----Principle of objectivity----the object contains an objectivity that does
not depend on the subject----to force the two fundamentally unequal interval
square to be absolutely equal to each other, i.e.,
Δs2≡Δs’2 (7)
Then bring the formula(5)and(6)into the above formulae, while V = r/(t’ +Δt),υ= r’/t’, and r ≡ r, it can be simply deduced as follows:
![]() (8)
(8)
and
![]() (9)
(9)
Again by some mathematic deductions (Omitted, please refer to [5] for
details),a transformation relation of the Generalize Space-Time Relativity will be
obtained as follows:
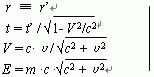 (10)
(10)
Those who are conversant with Einstein’s relativity would find out, not only is the time and space coordinates transformation is fundamentally different from Einstein’s special theory of relativity, but the velocity(V andυ)and the energy(E) transformation formulae are entirely different from Einstein’s special theory of relativity.
VI Problems in Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity and Modern Geometry
For the above-mentioned plane case,some
people may refuse to take my view that the time processes as recorded by A and B are
different or do not agree at all to that the flight time recorded by A is defined as t = t’
+Δt, but insistently follow Einstein’s view that the flight velocity for both
A and B are completely the same, i.e., V ≡υ, and hold the opinion that the “constriction”
of t’ and r’ is genuine. If these views are taken, it means to accept that A does not
need any signal transmission before he can tell, in absolute synchronism, the exact time
of the plane’s arrival in New York. However, based the touch action principle and the
finiteness of the signal transmission velocity, we can say for sure that it is absolutely
impossible for A to tell the exact time of the plane’s arrive in New York in absolute
synchronism. In contrast, if A can tell, in absolute synchronism, the exact time of the
plane’s arrival in New York, he must be using his “absolute thought” to deduce the
exact arrival time, hence not breaking away the time concept of absolute simultaneity.
It should be admitted that this erroneous space-time concept did not start with Einstein.
Dated back to 2300 years ago, in Euclid geometry, there were similar mistaken concepts. As
it is known to all, in geometry, people only takes into account the space relation of a
geometric figure without considering the possible effect of the size of the geometric
figure over the problem. Indeed, if what we study is a pure geometric relation, it causes
no effect on the problem itself to use the ideation featuring infinite velocity to create
geometric abstraction, but if what we study is the space-time relation formulated by the
object movement (e.g., inertial movement), consideration would have to be given to the
priority of sequence of the space locations represented by the “points” and “segments”
in the geometric figure (such as points A, B, C… and segments AB, BC, CA…), that
priority being caused by the finiteness of the movement velocity. In other words, in
relativity, under circumstances where the finiteness of the movement velocity has to be
considered, Euclid’s geometric theories (or other geometric theories) should be directly
applied to deal with the space-time relation that exists actually. For instance, certain
line segment (AB) is a space-time relation formulated by an object (or particle) moving
from A to B in uniform rectilinear motion, so taking into account the finiteness of the
object moving velocity, a priority of the time sequence would lie between the two points
on the line segment AB and the minimum value of the time sequence just equals the
resulting value of the distance (r) between the two points divided by the velocity of
light (c), i.e., Δt = r/c. So, geometric abstraction can only be unconditionally
valid in pure geometry. ----This is a mathematic and physical concept that needs
us to consider and update carefully.
With regard to Einstein’s general theory of relativity, we say that the space-time concept which assumes “space has a geometric nature” is, from the logic point of view, an erroneous cognition whereby the universality is mistaken into peculiarity because “space” and “time” are the highest abstraction of the object’s “existing form” and “moving process”, respectively representing the universality of the existing form and moving process of the object. Just as Engels stated,“Just like the concept of number, the concept of form is obtained entirely from the outer world and is not generated out of pure thought in the mind. First, there must exist objects in definite forms and, after comparing these forms, the concept of form can be established. The subjects of pure mathematics are the space form and quantity relations of the actual world, and are therefore the very actual materials. ----But, to study these forms and relations in pure conditions, they must be separated from their own contents, which are to be put aside as things of no importance. By this, we can obtain points with no length, width and height and lines with no thickness and breadth, a and b, x and y, i.e., constant and variable. (Refer to [6]. Page 77)” Therefore, to say that space contains “geometric nature”----either flat or twisted----is to put individuality (peculiarity) into universality, i.e., universality is mistaken peculiarity. This way of viewing universality from the aspect of form and juxtaposing the universality and the peculiarity won’t go anywhere even in daily life. For instance, Hegel clearly stated, “if universality is only viewed from the aspect of form and is juxtaposed with peculiarity, then universality itself would fall into some thing peculiar. The method of juxtaposition is not appropriate and does not go anywhere when applied even to things in daily life. For example, in daily life, nobody would just ask for fruit instead of cherry, pear and grape because they are just cherry, pear and grape but not fruit. (Refer to [4], page 55)” In reality, according daily experience, nobody would think that cherry, pear and grape are just themselves but do not belong to “fruit”. In much the same way, we should refrain from regarding the known relation and mutual locations of the objects just as the known relation and mutual locations of the things in question, but should think that they are the objects belonging to the space for they occupy a space location. However, there does exist an erroneous cognition in the aspect of the Einstein’s general theory of relativity and the modern geometry. So, the general theory of relativity cannot be taken as a firm space-time theory. (For full understanding of the application of Generalized Space-Time Relativity in the field of gravitation--- theory of gravitation, refer to chapter 2 of [5]). It can be said: “flat space” is only the precondition of Euclid’s geometric axiom while “twisted space” with negative curvature is the precondition of Ropachewsky’s geometric axiom. Therefore, all “geometric axioms” are conditional and belonging to the scope of relative truth, the same as “objective truth” in other fields.
VII Understand the Relativity of Simultaneity from Law of Unity of Opposites
According to the fundamentals of the dialectical materialism, we say, in the matter of time, concrete identity is concrete simultaneity, but concrete simultaneity means that simultaneity contains non-simultaneity. As it is said, in all things, if there is no “difference” as the opposite to “identity”, they would not develop into “difference” from “identity”----This the law of the unity of opposites of the dialectical materialism, the same goes with simultaneity. Let’s take a visualized example; “living” and “death” is a pair of contradictions. If a living organism does contain the seed of death, it would never evolve from “living” to “dead”. In the same way, a moving thing at the starting point of both space and time, if not containing a “concrete simultaneity”, would never develop from simultaneity (i.e. t = t’) to non-simultaneity (i.e. t≠t’) in the process of movement. So Hegel said, “concept and idea are indeed identical to their selves, but the reason why they are identical is that they simultaneously contain difference within their selves. (Refer to [4]. Page 248)”
Entirely different from Einstein theory, Generalized Space-Time Relativity holds the view that the objective cause leading to concrete simultaneity is the finiteness of action principle transmit velocity rather than the subjective random of selection on the coordinate system. If transmit velocity of action principle is infinite, time coordinates will have absolute simultaneity between any two remote coordinate frames, then in whatever space location the observer stands and observes the movement of the object (or particle), it won’t be such that t = t’ (at the starting point of movement) transforms to t ≠t’(leaving the starting point of movement), so on and so forth. Generally, if coordinate transformation is not understood according to the above conception, people would believe that “Lorentz’s constriction” really happens to the space coordinates and the time coordinates during movement on the movement frame, and must deny the objective substantiality of the space and time and go even far to think that “Space and time are not objective existence but that perceived through the perceptual intuition form of human beings”. ----This is Mach’s relativist space-time concept and pure subjective idealism.
VIII Conclusion
There are three essential points in
determining whether a physical theory is right or not. The first is logical and conceptive
soundness, the second is the rigidity of mathematic deduction, and the third is the
effectiveness of its practical application (including predicting new phenomenon). But
Einstein’s theory is just problematic in this aspect. Therefore, we should not use the
great achievement of Einstein’s theory to conceal its logic and conceptive errors. On
account of this, following Engels and Lenin’s dialectical materialist space-time concept
and on the basis of summarizing the new achievements in modern mathematics and physics, I
propose the Generalized Space-Time Relativity. Frankly speaking, this is a brand new
space-time theory. Starting from this theory, we can not only radically overcome the logic
and conceptive errors lying in Einstein’s theory while remaining able to solve the
space-time issues already dealt with by Einstein’s theory, but can also solve some
space-time issues that was unable to be dealt with by Einstein’s theory. To be honest,
this is a space-time theory with broad development prospect.
References literature:
[1]《Materialism and Empirical Criticism》, written by Lenin, People’s Publishing
House, Beijing, July 1950,
first Issue.
[2]《Introduction to Future Metaphysics》, written by Kant, Translated by Pang Jingren,
Commerce Printing
House, Beijing, Aug. 1978, First Issue.
[3]《Theories of Space, Time and Gravity》, written by B.A. Fock, Translated by Zhou
Peiyuan, Zhu Jiazhen
and Cai Shutang, Science Publishing House, Beijing, July. 1965, first Issue.
[4]《Small logic》, written by F. Hegel, Translated by He Ling, Commerce Printing House,
Beijing, July 1980,
Second Issue.
[5]《Generalized Space-Time Relativity 》, written by Xia Xingguang, People’s
Communications
Publishing House, Beijing, Jan.2003, First Issue.
[6]《Selected Works of Marks and Engels》,Vol. 3, People’s Publishing House, Beijing,
May 1972, First Issue.
![]() 版权所有,保留一切权力,未经授权使用将追究法律责任 版权说明 © Copyright Authors
版权所有,保留一切权力,未经授权使用将追究法律责任 版权说明 © Copyright Authors
物理科学探疑