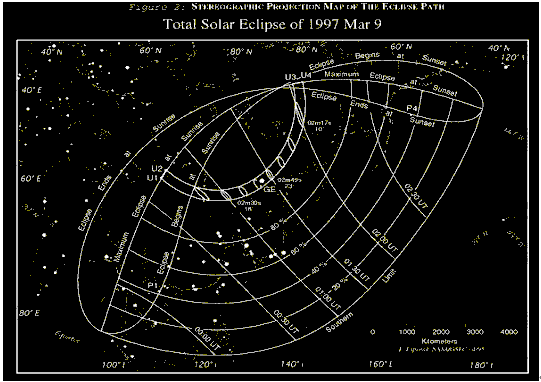
Figure 1 Total Solar Eclipse of 1997 March 9
Induction Gravity From Temporal Variations
in Gravity Field
During Total Solar Eclipse
Chen Shouyuan
(Shandong Normal University, 250014, Jinan , P.R. China
Tel: 0531-6189538,E-mail:chensy@beelink.com)
ABSTRACT: The temporal variation in the gravity field during total eclipse of 1997 March 9 occurs with the onset of the solar eclipse and the departure. The principle of temporal variation in gravity field maybe similar to Faraday’s electromagnet induction, the change of motion induces force field.
KEYWORDS: Gravitation variation; solar eclipse; induction gravity
1 Total Solar Eclipse of 1997 March 9
On Sunday, 1997 March 9, a total eclipse of the Sun was visible from parts of eastern Asia. The path of the Moon's umbral shadow begins in eastern Kazakhstan, and travels through Mongolia and eastern Siberia where it swings northward to end at sunset in the Arctic Ocean. A partial eclipse will be seen within the much broader path of the Moon's penumbral shadow, which includes eastern Asia, the northern Pacific and the northwest corner of North America (Figure1)[1].

Figure 1 Total Solar Eclipse of 1997 March 9
2 Precise measurement of gravity variations during a total solar eclipse
The variations of gravity were measured with a high precision LaCoste-Romberg D gravimeter during the total solar eclipse of 1997 march 9 to investigate the effect of a solar eclipse on the gravitational field. The observed anomaly (7.0±2.7)×10–8 m/s2during the eclipse implies that there may be a shielding property of gravitation [2].
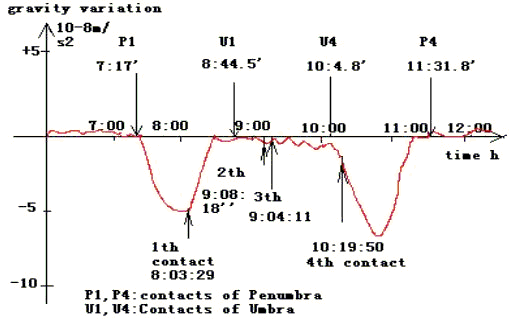
Figure 2 Temporal variation in gravity field during solar eclipse on 9 March 1997
This observation and measurement during the total eclipse were carried out in Moho ,China (53°29’N, 122°20’E).From Figure 2, we can see that the temporal variation in the gravity field occurs with the onset of the solar eclipse and the departure .
3 Faraday's Law of Induction
Faraday made the first step in the discovery of the great law of electromagnetic induction that new bears his name. The electric current was not caused by the magnetic field, but by a change in the magnetic field. We have already seen that faraday associated an electric current with a changing magnetic field; a change in the magnetic flux through a circuit produces an electromotive force around the circuit. Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction is :
![]() (1)
(1)
The Faraday's law is the changing magnetic field creates electric field.
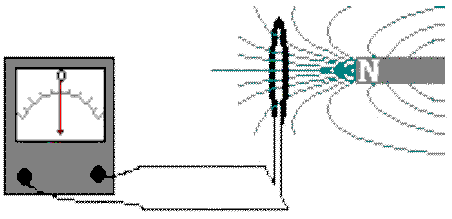
Figure 3(a) Faraday's Magnetic Field Induction Experiment
In this picture an ammeter is connected in the circuit of a conducting loop. When the bar magnet is moved closer to, or farther from, the loop, an electromotive force (emf) is induced in the loop. The ammeter indicates currents in different directions depending on the relative motion of magnet and loop. Notice that, when the magnet stops moving, the current returns to zero as indicated by the ammeter
A magnet thrust into a coil produces a noticable deviation on a table galvanometer. Or the coil can be moved over the magnet:
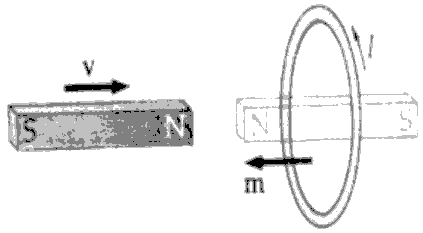
Figure 3(b) Faraday's Magnetic Field Induction Experiment
4 the temporal variation in the gravity field occurs with the onset of the solar eclipse and the departure
A total solar eclipse requires the umbra of the Moon's shadow to touch the surface of the Earth. Because of the relative sizes of the Moon and Sun and their relative distances from Earth, the path of totality is usually very narrow (hundreds of kilometers across). The following figure illustrates the path of totality produced by the umbra of the Moon's shadow [1].
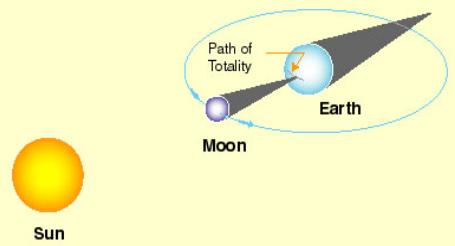
Figure 4 Solar eclipse (not to scale)
The temporal variation in the gravity field occurs with the onset of the solar eclipse and the departure. As the moon thrusts between Earth and Sun. the temporal variation occurs. Or the moon can be moved out.(to see Figure 5)
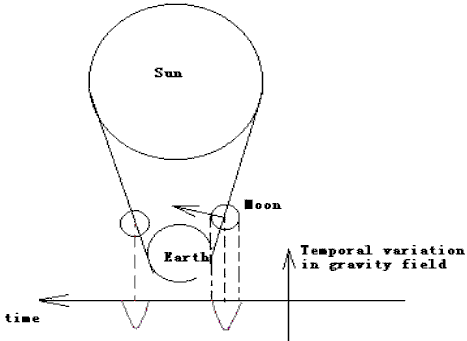
Figure 5 gravity variation with solar eclipse
5 principle of gravity variation
Faraday ‘s induction law: when the change of electricity is induced induction fields. Newton second law: the change of motion is proportional to the motive force impressed; and is made in the direction of the right line in which that force is impressed. We discuss when the motion state of any object changes, is the induction field inducing?
any body is moved closer to, or farther from, the gravity loop, an induction force (so called induction gravity) is induced in the loop. To see Figure 6
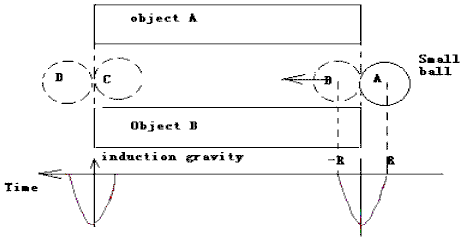
Figure 6 induction gravity model

REFERENCES
[1]NASA WWW
[2] Qian-shen Wang, Xin-she Yang. Precise measurement of gravity variations during a total
solar eclipse[J]. Physics Review 2000,D(62):41101~41103
![]() 版权所有,保留一切权力,未经授权使用将追究法律责任 版权说明
© Copyright Authors
版权所有,保留一切权力,未经授权使用将追究法律责任 版权说明
© Copyright Authors
物理科学探疑